

Let us use this procedure to solve inequalities of different types. But to solve any other complex inequality, we have to use the following process. The process of solving inequalities mentioned above works for a simple linear inequality. Why? This is because we have multiplied both sides of the inequality by a negative number.
The rules of inequalities are summarized in the following table.

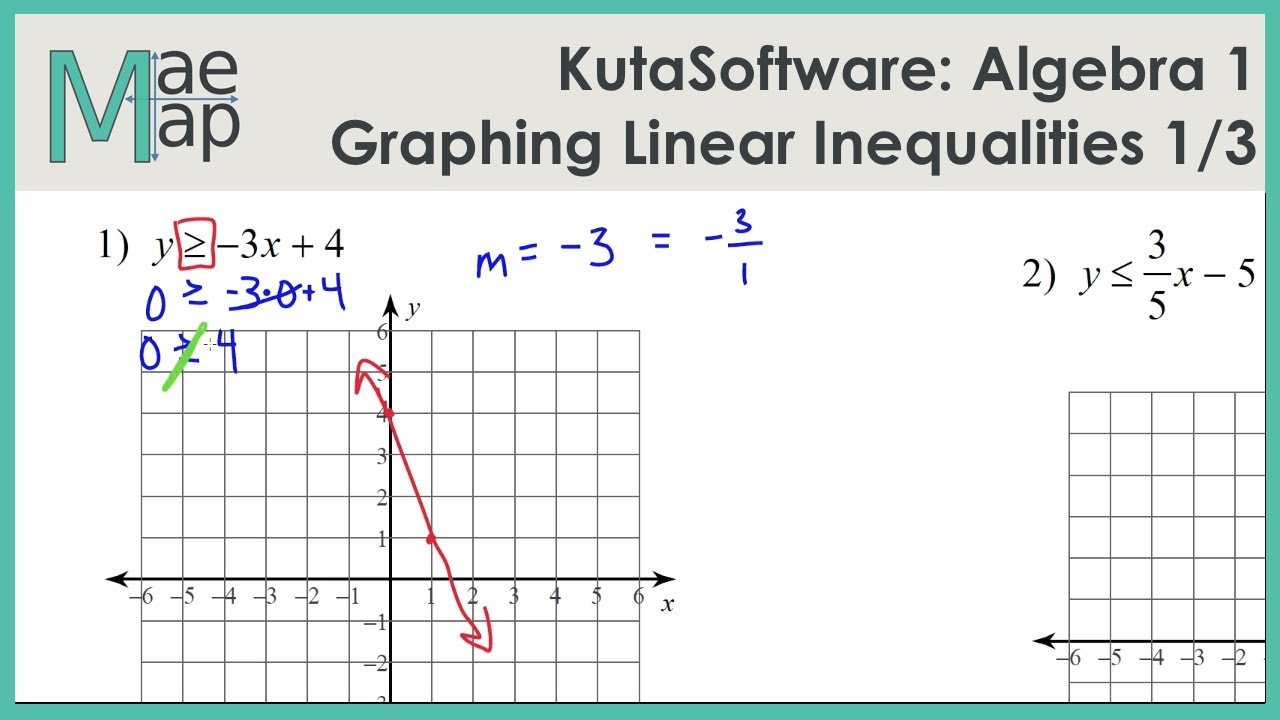
Taking a square root will not change the inequality. Putting minuses in front of p and q changes the direction of the inequality.Ī square of a number is always greater than or equal to zero p 2 ≥ 0.Įxample: (4) 2= 16, (−4) 2 = 16, (0) 2 = 0 Inequalities Rule 8 Positive case example: Oggy's score of 5 is lower than Mia's score of 9 (p −q. If you multiply both p and q by a negative number, the inequality swaps: p qd (inequality swaps) If you multiply numbers p and q by a positive number, there is no change in inequality. So, the addition and subtraction of the same value to both p and q will not change the inequality. Inequalities Rule 3Īdding the number d to both sides of inequality: If p q, then p + d > q + d, and Inequalities Rule 2Įxample: Oggy is older than Mia, so Mia is younger than Oggy. When inequalities are linked up you can jump over the middle inequality.Įxample: If Oggy is older than Mia and Mia is older than Cherry, then Oggy must be older than Cherry. Here are some listed with inequalities examples. There are different types of inequalities. p ≥ q means that p is greater than or equal to q.p ≤ q means that p is less than or equal to q.One of the things may be less than, greater than, less than or equal to, or greater than or equal to the other things. The meaning of inequality is to say that two things are NOT equal. This is a practical scenario related to inequalities. But you do know her age should be less than or equal to 12, so it can be written as Olivia's Age ≤ 12. How old is Olivia? You don't know the age of Olivia, because it doesn't say "equals". The equal sign in between is replaced by less than (or less than or equal to), greater than (or greater than or equal to), or not equal to sign. In inequality, unlike in equations, we compare two values. We shade below the line.Inequalities are the mathematical expressions in which both sides are not equal. Since the inequality is ≤, the wanted region is below the line. Rewrite the inequality 2 x – 3 y ≥ 6 as y ≤ x – 2. All the points below the line are represented by the inequality y 2 x –1 and the region below the line is represented by y then we draw a dotted line.Īfter drawing the line, we need to shade the unwanted region. In the following diagram, all the points above the line y = 1 are represented by the inequality y > 1. We also have a systems of inequalities calculator that can display the shaded region that satisfies all the given inequalities.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
